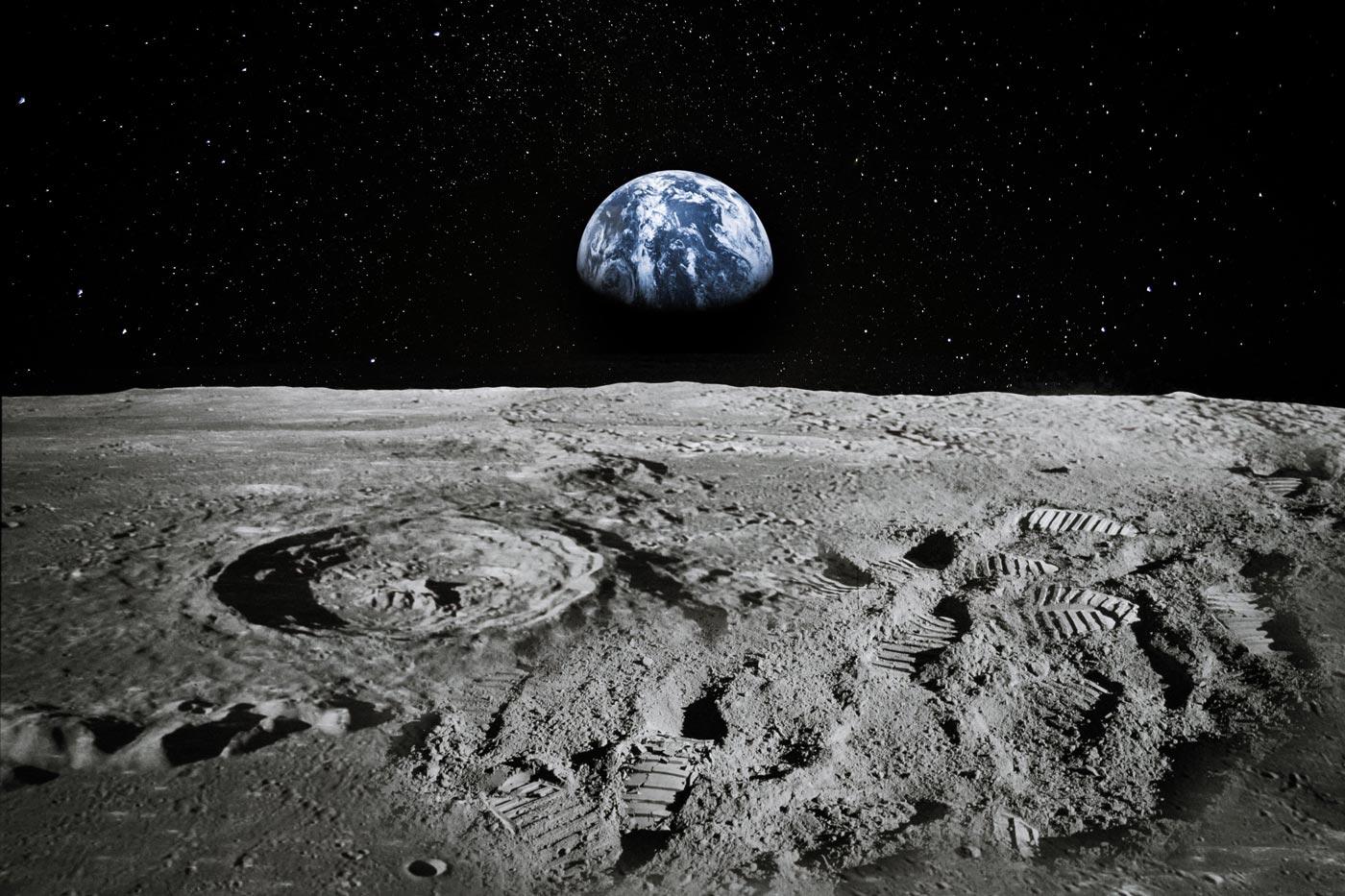
The moon is a natural satellite of the earth, consisting of rock, dust, and ice. It was formed about 4.5 billion years ago, soon after the formation of the earth. When a large planetoid collided with the earth, the resulting debris formed a ring around the earth. This ring eventually coalesced to form the moon.
The moon’s diameter is about one-fourth that of the earth, and its mass is about 1/81 that of the earth. The moon orbits the earth at an average distance of 384,400 km (238,900 mi) and completes one orbit in 27.3 days. The side of the moon facing the earth is called the near side, while the far side is called the dark side because it is permanently turned away from the earth and receives very little sunlight.
The surface of the moon is covered with craters, mountains, and valleys. The most prominent feature on the near side is a dark area called the Mare Imbrium (Sea of Showers), which is actually a vast lava plain formed by volcanic eruptions about 3.9 billion years ago. The far side of the moon, which is much rougher in appearance, has been heavily cratered by collisions with meteoroids.
The moon has a profound effect on the earth. Its gravitational pull creates the tides in the earth’s oceans. The moon also stabilizes the earth’s rotation on its axis, which helps to create a more stable climate on the earth.
The average distance from the earth to the moon is 384,400 km (238,900 mi). The moon’s orbit around the earth is not perfectly circular, so the actual distance between the two bodies varies. At its closest point (called perigee), the moon is about 356,400 km (221,500 mi) from the earth, while at its farthest point (called apogee), it is about 406,700 km (252,700 mi) from the earth. The moon’s orbit is also tilted with respect to the earth’s orbit around the sun, so that the moon sometimes appears closer to the sun than the earth (this is called perihelion) and sometimes appears farther from the sun than the earth (this is called aphelion).
Scientists believe that the moon has water ice in its permanently shadowed craters near the poles. They also believe that there may be water ice in the lunar regolith (the loose surface material on the moon’s surface). In 2009, the LCROSS mission confirmed the presence of water ice on the moon.
The moon has no atmosphere, so there is no wind or weather on the moon. The temperature on the moon’s surface varies from about -173 degrees Celsius (-280 degrees Fahrenheit) at night to about 123 degrees Celsius (253 degrees Fahrenheit) during the day.
The moon is a fascinating place, and scientists are still learning new things about it every day.