Living things interact with their environments. This includes cells, which take in nutrients and expel waste. They do this through active and passive transport. Active transport requires energy, while passive transport does not. Examples of active transport include cells taking in glucose against a concentration gradient. Meaning that the cell must use energy to bring the glucose (sugar) into the cell.
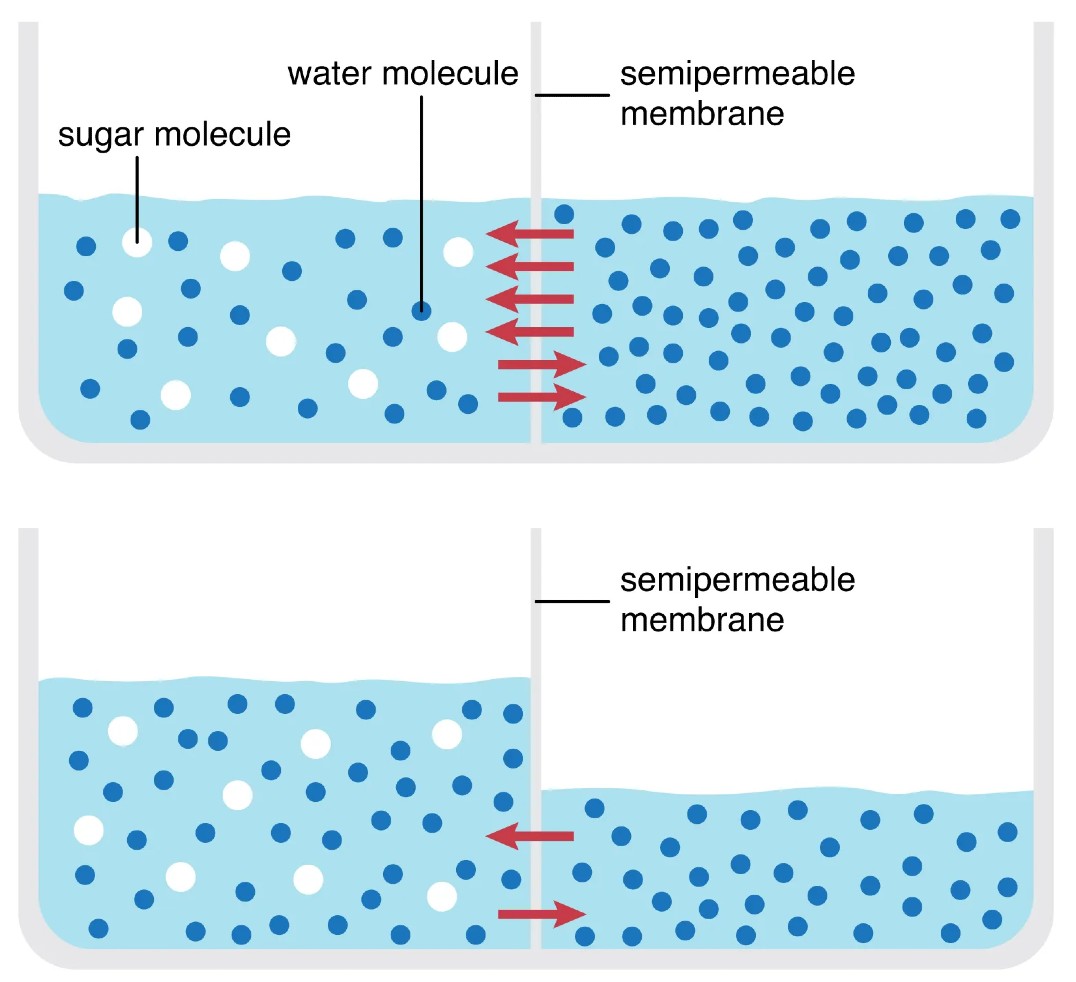
Examples of passive transport include osmosis. Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This can happen across a semipermeable membrane, such as a cell membrane. When a cell is placed in a solution, water will move into or out of the cell depending on the concentration gradient. If the solution outside the cell has a higher concentration of solutes than the cytoplasm inside the cell, then water will move into the cell. This will cause the cell to swell. Conversely, if the solution outside the cell has a lower concentration of solutes than the cytoplasm inside the cell, then water will move out of the cell. This will cause the cell to shrink.
A solute refers to any substance that is dissolved in a solution. The concentration gradient is the difference in solute concentration between two areas. A common example of solutes is salt. Think of it as though the water is attracted to the solute. Thus, if there is more salt outside a cell, then water will move toward the solute. In other words it will leave the cell and travel out. If there is more salt inside the cell then water will move toward this salt. this time entering the cells, possibly bursting.
Why can’t you drink saltwater? The high concentration of salt outside of cells causes water to leave the cells in your body by osmosis. This causes dehydration and eventually death.
Osmosis is important for plant cells. They have a cell wall that prevents them from bursting when water enters the cell by osmosis. Animal cells do not have a cell wall and will burst if placed in a solution that has a higher concentration of water molecules than the cytoplasm inside the cell.
So, to recap: osmosis is the movement of water molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration across a semipermeable membrane. This can cause a cell to swell or shrink, depending on the relative concentrations of solutes inside and outside the cell. Osmosis is important for plant cells, as they have a cell wall that prevents them from bursting. Animal cells do not have a cell wall and will burst if placed in a solution that has a higher concentration of water molecules than the cytoplasm inside the cell.