Humidity
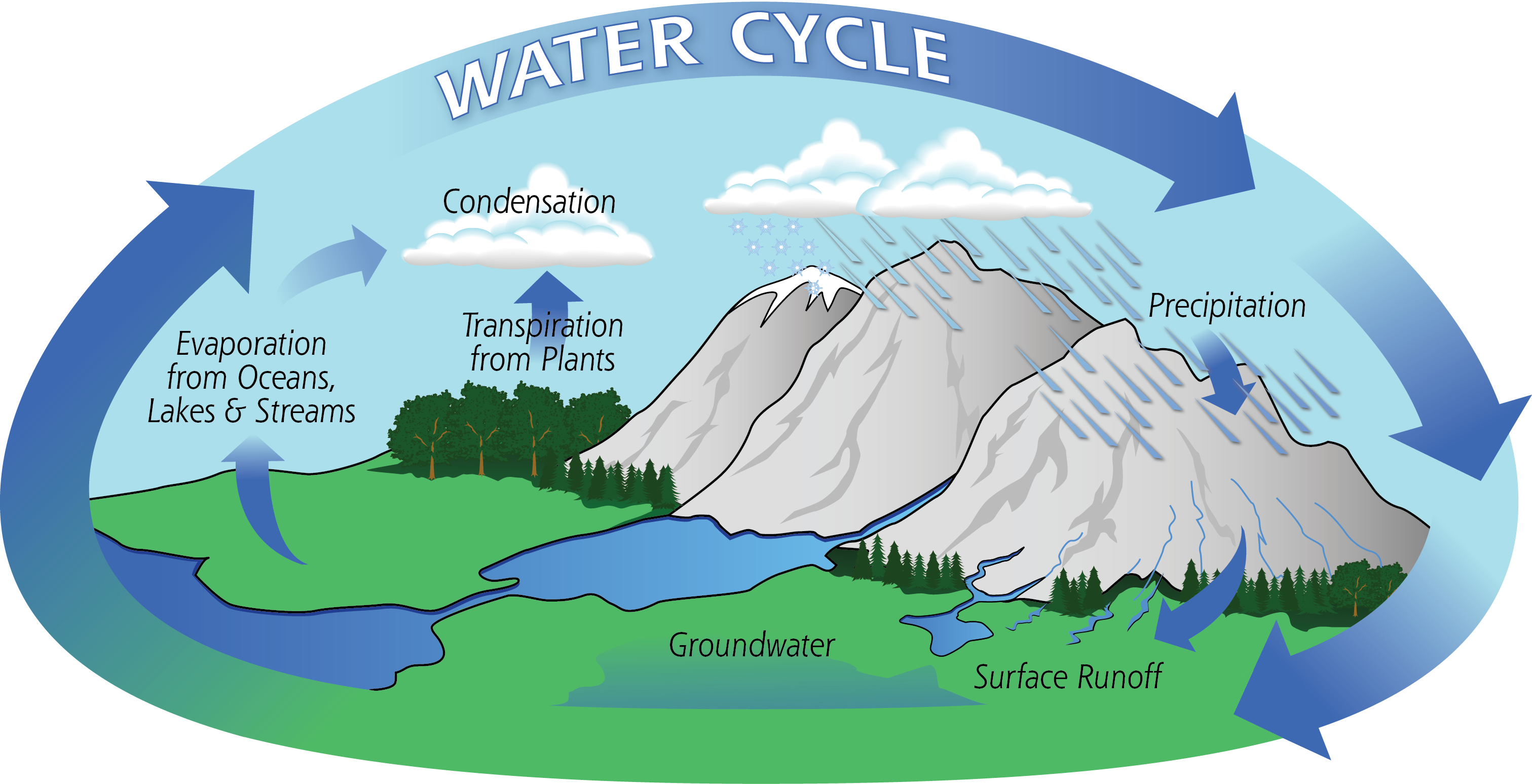
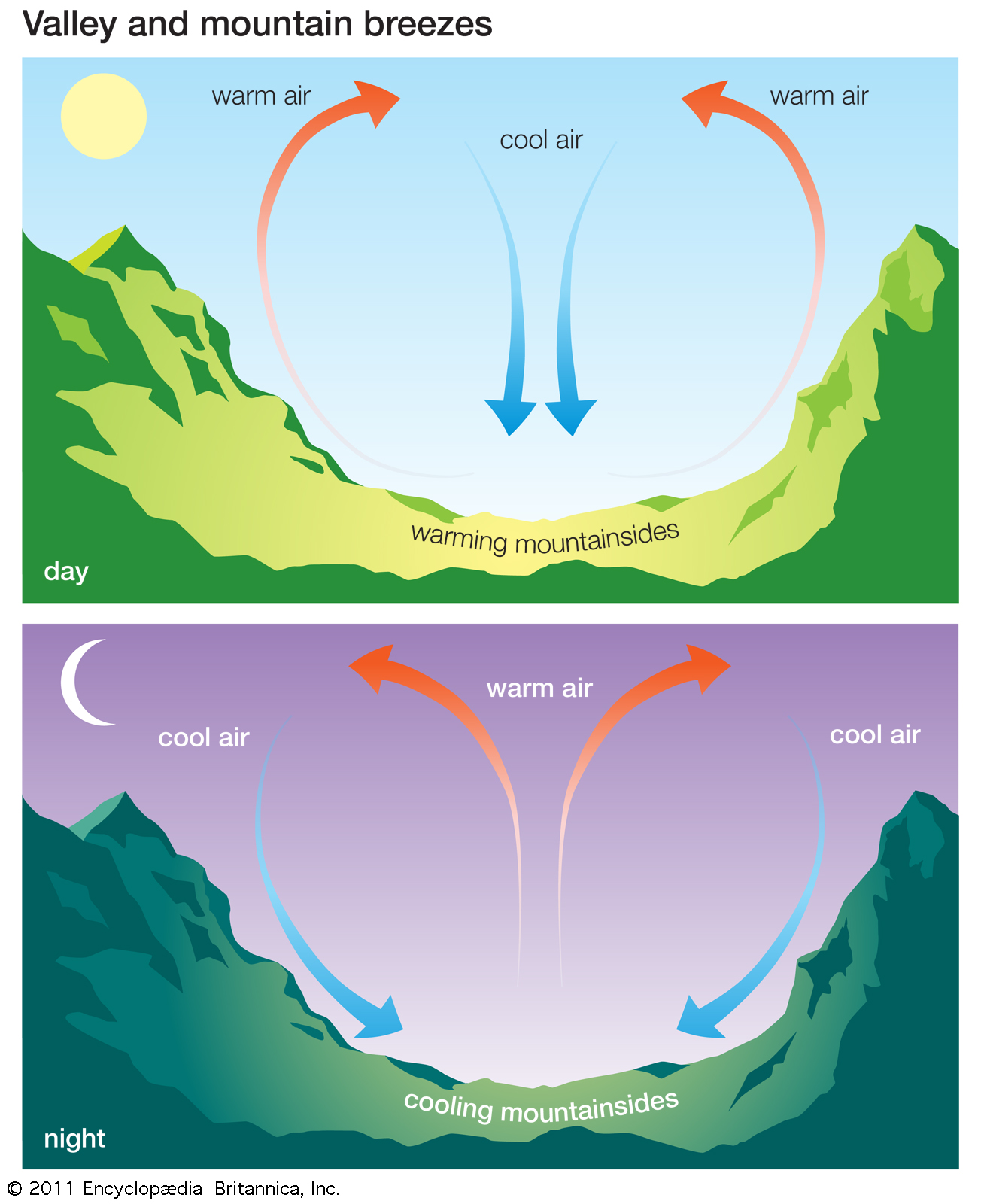
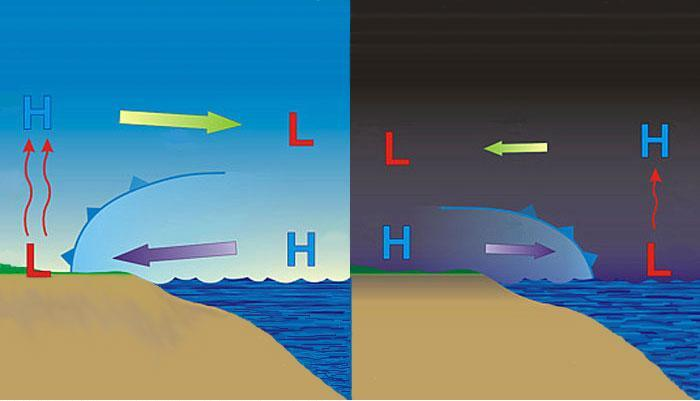
The amount of water vapor in the air is referred to as humidity. The more water that is in the air there is, the higher we say that the humidity has risen. Humidity can be measured in a number of ways. These include absolute humidity, specific humidity, and relative humidity. Absolute and specific humidity measure […]