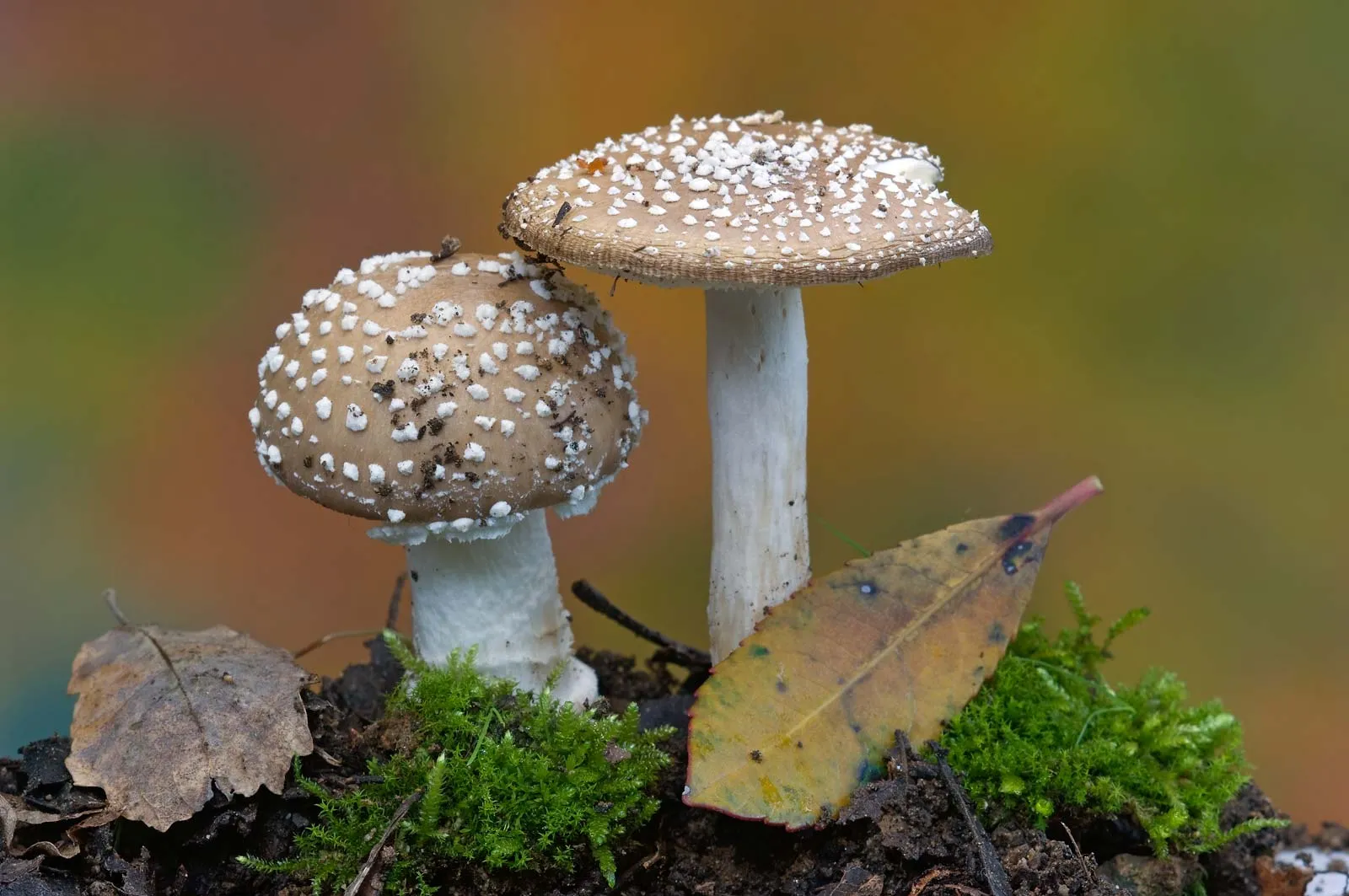
Fungi are a type of organism that is classified separately from plants. They are distinguished by their lack of chlorophyll, which allows them to obtain nutrients in different ways than plants. Many fungi live in symbiotic relationships with other organisms, such as trees, and help to decompose dead matter.
Decomposers are organisms that break down complex organic matter into simpler inorganic compounds. This process is important for the recycling of nutrients in ecosystems. Decomposers are usually bacteria or fungi.
Fungi are an important type of decomposer. They help to break down dead plant and animal matter, returning essential nutrients to the soil. This is important for the health of ecosystems. Fungi also play a role in the food chain, as many animals eat fungi, such as mushrooms.
Humans also benefit from fungi. Some types of fungi are used to make food, such as yeast in bread and the fermentation of beer and wine. Other fungi are used in medicine, such as penicillin. Fungi are an important part of the natural world and play a vital role in the health of ecosystems.
There are four types of fungi.
· Zygomycota- Zygomycota are fungi that form sexually by the union of two hyphae. They produce small, round spores called sporangiophores.
· Ascomycota- Ascomycota are fungi that produce spores in sacs called asci. They can reproduce asexually by producing spores, or sexually by the union of two hyphae.
· Basidiomycota- Basidiomycota are fungi that produce spores on club-shaped structures called basidia. They reproduce sexually by the union of two hyphae.
· Deuteromycota- Deuteromycota are fungi that do not form spores. They reproduce asexually by producing hyphae with swellings called conidiophores.
Fungi can cause diseases such as athlete’s foot, ringworm, and candidiasis. These fungal infections spread by contact with contaminated surfaces or by inhalation of spores. Treatment usually involves antifungal medications.
Fungi are an important part of the natural world and play a vital role in the health of ecosystems. They are essential for the decomposition of dead matter and the recycling of nutrients. Fungi also provide humans with food, medicine, and other benefits.
Fungi belong to their own kingdom. They are neither plant, nor animal, but instead, share traits with both. Like plants, they have cell walls and many take in nutrients through root-like structures. Like animals they are heterotrophs meaning that they cannot produce their own food. Like both plants and animals, they are multicellular. Meaning that they are made up of more than one cell.