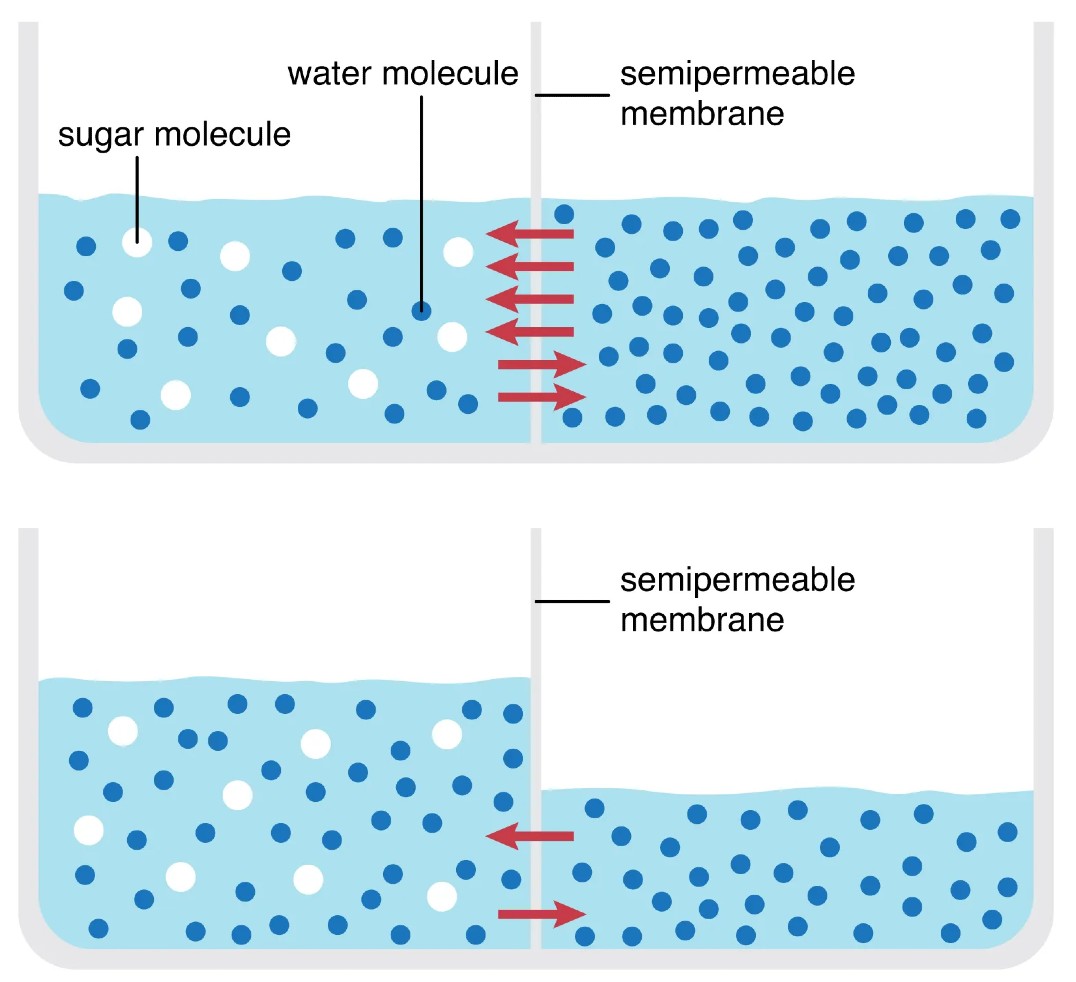
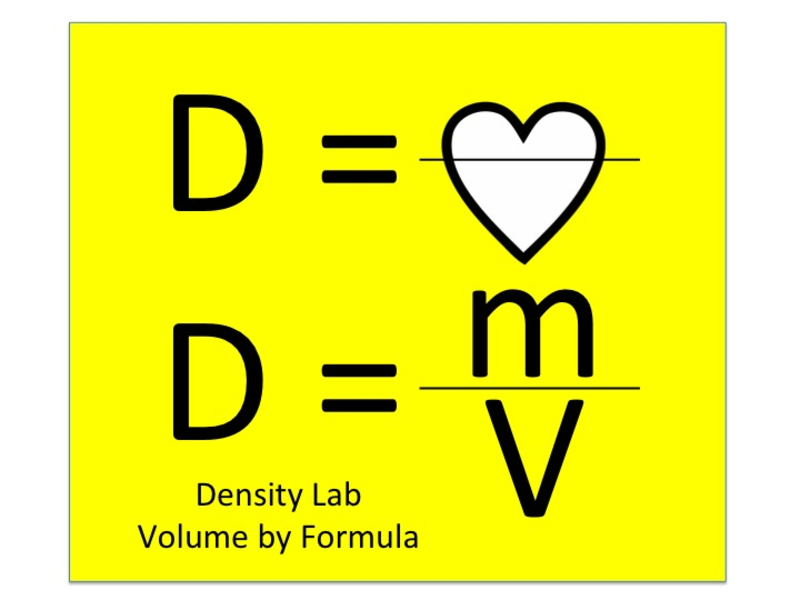
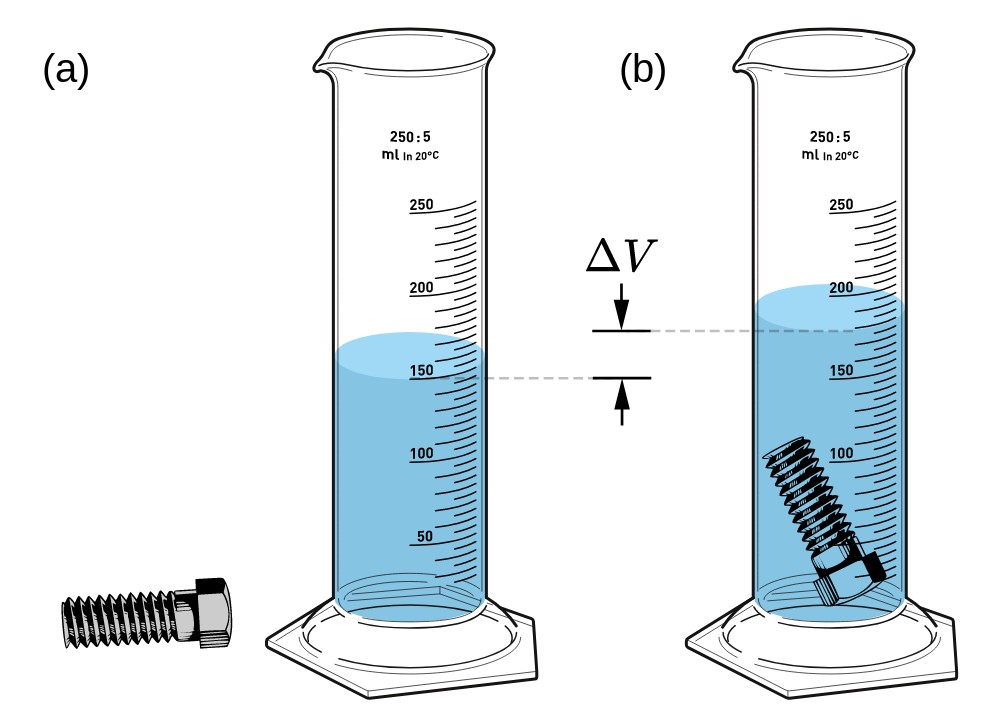
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
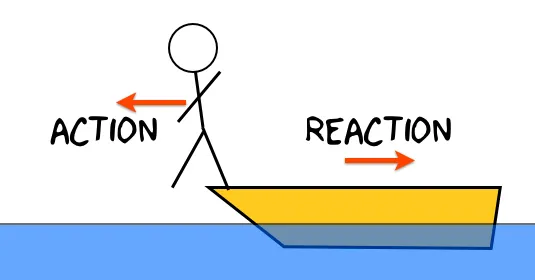
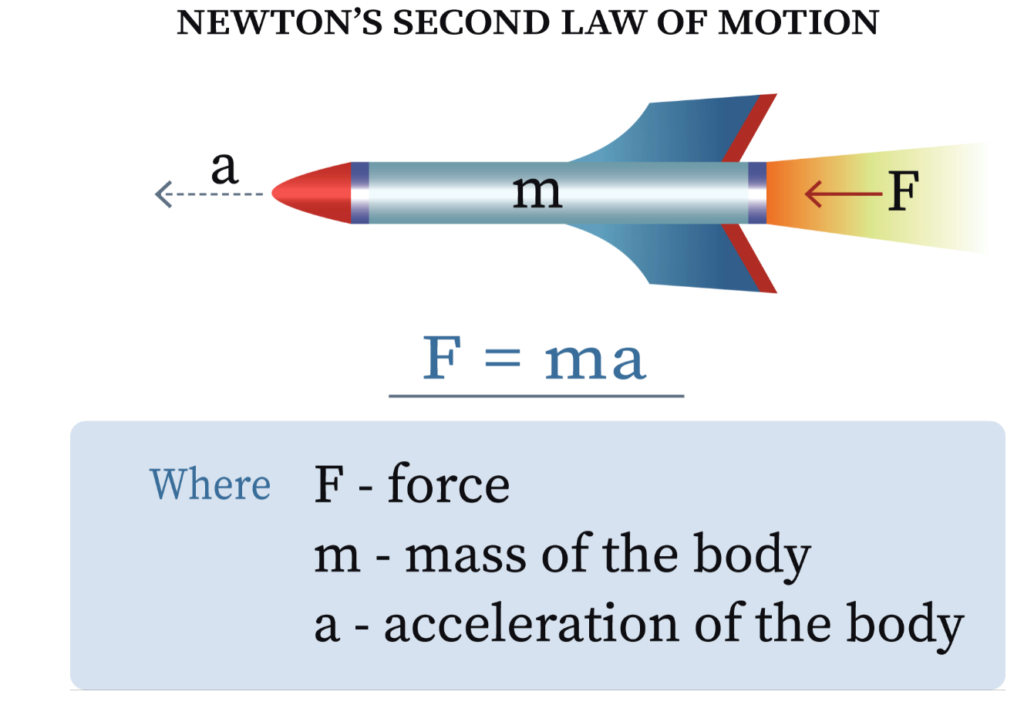
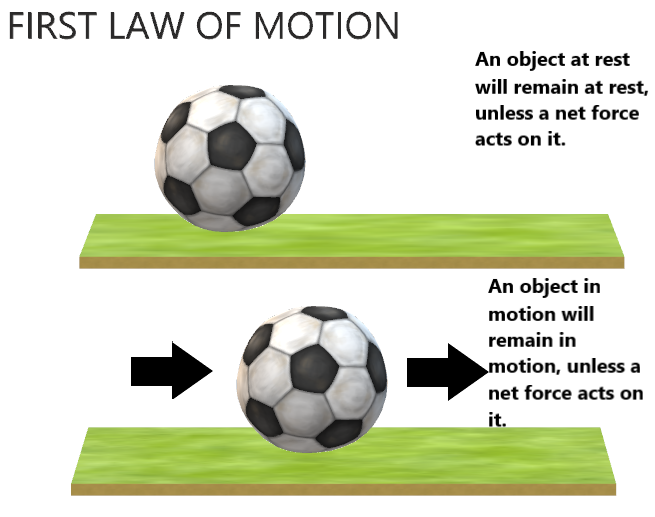
Issac Newton’s Third Law of Motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This law is the basis for many things we see in everyday life, from the way a rocket propels itself through the air to the way a person pushes against the ground to walk. It is also […]