Everything in the Universe has gravity, including you! Gravity attracts objects toward each other. The larger an object is, the more gravity it has. For example, a star, like the Sun has significantly more gravity than an asteroid.
Like all fields, including magnetism, static electricity, and yes, gravity, the attractive force increases the closer you get to the object. Thus, while a star on the other side of the Galaxy has far more gravity than the Earth, we are much more impacted by the gravity of the Earth than the gravity of that star.
Likewise, the gravity of the Sun does tug on us, as does the gravity of the Moon. However, because we are so much closer to the Earth we remain bound to it.
As the Moon orbits the Earth, rocks, air, and water are all tugged toward the Moon’s gravity. However, the rocks can’t really move very much. This is not the case though for the atmosphere and water, which are both fluid. In science a fluid is anything where the molecules can freely slide past one another.
Because the atmosphere and oceans are both fluid the molecules tend to move, and many of them are pulled, or dragged about by the gravity of the moon, creating what we call tides.
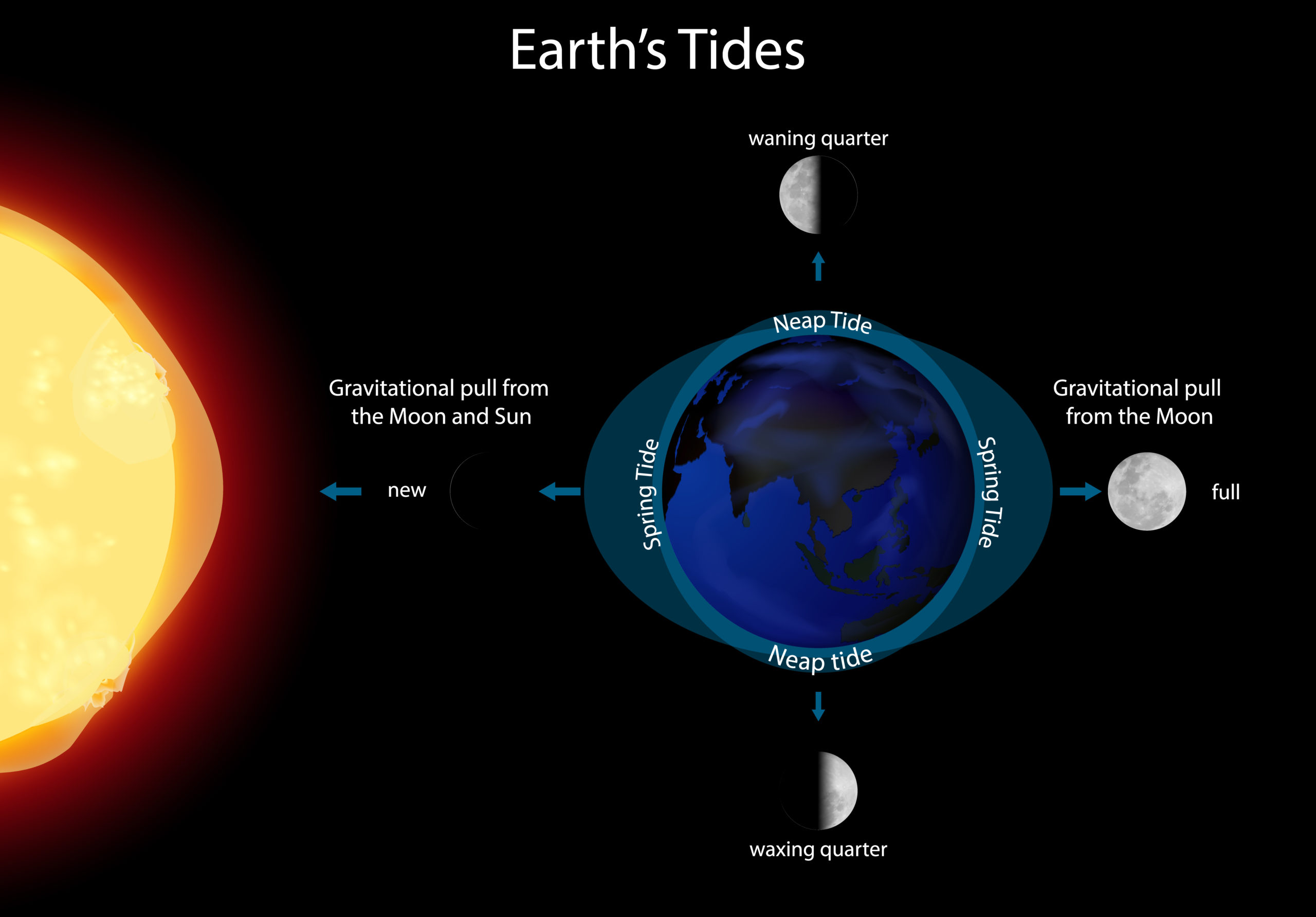
Tides occur when the gravity of the moon (or sometimes the sun) pulls on the bodies of water on Earth, causing the water to bulge out in the direction of the pull.
There are two types of tides: Spring Tides and Neap Tides. Spring tides occur when the Earth, moon, and sun are all lined up. The extra pull of the sun’s gravity joins with the moon’s gravity to create higher than normal high tides and lower than normal low tides.
Neap tides occur when the moon is at first or third quarter phase (halfway between new or full). At these times, the sun and moon are at right angles to each other with respect to the Earth. The sun partially cancels out the effect of the moon’s gravity, resulting in smaller than normal tides.
In general, there are two high tides and two low tides every day. However, the height of the tides depends on a number of factors including the alignment of the sun, moon, and Earth, the size of the ocean basin, and the shape of the coastline.
For example, tides are usually much higher in shallow bays than in deep oceans. This is because there is less water to move out of the way when the tide comes in.
The time between high and low tide, called the tidal period, is about 12 hours and 25 minutes. This is the time it takes for the water at the farthest point from the moon to come back around and line up with the moon again.
However, because the Earth is also rotating on its axis as it orbits the sun, high tide occurs about 50 minutes later each day. So, if high tide is at 6:00 am today, it will be about 6:50 am tomorrow.
Tides can have a significant impact on coastal areas, so it is important to be aware of the tidal pattern for your area. Tides can also be used to generate electricity, as well as to help transport goods and people.