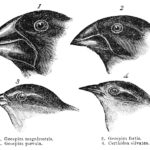
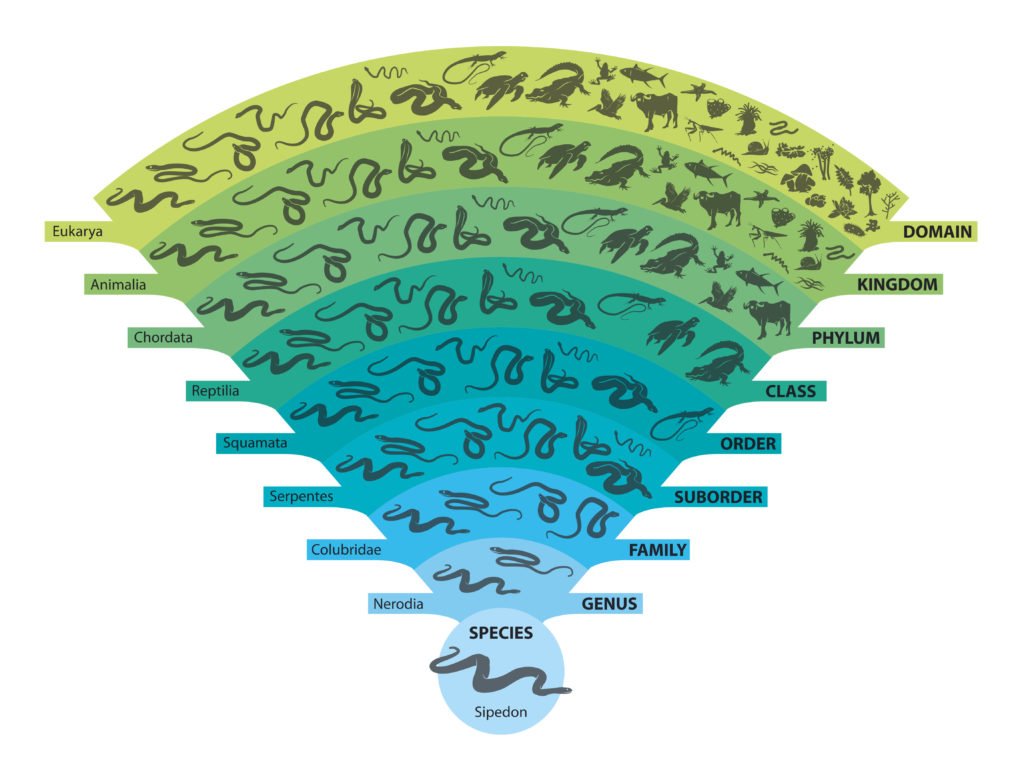
Living things are divided into six kingdoms of life based on how they are alike and how they are different. The largest of these kingdoms is the animal kingdom. Animals come in many different shapes and sizes. Some have exoskeletons, while others have no skeletons at all, and still others have highly evolved internal skeletons.
One of the most successful group of animals on Earth are the mammals. There are over 5,400 mammal species alive today.
Mammals are called vertebrates because they have backbones. They also share several other traits such as air-breathing, having hair or fur on the outside of their bodies, and most give birth to live young. Instead of laying eggs as do many other animals.
Mammals are warm-blooded, which means their bodies maintain a fairly constant temperature.
Like all other animals that live on Earth, mammals are made up of cells and tissues that work together to support the mammal’s life processes. Some mammal species even have special features that help them survive better in their natural habitats.
Mammals can live in nearly any environment, from swamps to deserts to arctic tundra.
While some mammal species are fairly small (such as shrews), others like the blue whale are the largest animals on Earth.
Some mammal traits that help them adapt to their surroundings include: Having live births; being able to fly, slither, swing from trees, swim in water, or live inside of caves. You can see that mammals have truly evolved to live under a wide variety of conditions.
In general, mammals must keep their body temperatures within a fairly narrow range. In cold weather, the mammal’s body produces more heat by shivering or through its food. Fur is also an adaptation found in some mammal species. All mammal mothers nurse their young with milk produced by mammary glands. Mammals also have bigger brains than creatures from other groups because of higher metabolic demands.
Mammals use stereoscopic vision, which means their eyes are spaced apart and each eye has a different picture projected onto it. Mammal eyes are also forward facing, which allows them to perceive distance very effectively.
The earliest vertebrates lived about 500 million years ago in the ocean. However, mammal evolution did not begin until over 200 million years after the first mammal-like reptiles appeared.
Around 100 million years ago mammal populations began to explode. At that time, mammal-like reptiles were among the most successful animals on the planet.
Mammals are now the dominant type of animal on land, with over 5,400 living species.
The mammal’s closest relatives are reptiles and birds. All three groups share many basic traits (for example, they all have backbones), but mammal traits are the most advanced.
Mammal means “one who suckles”, and describes creatures such as platypus and humans that have mammary glands used to feed their young. These mammal-like reptiles also had a diaphragm, an important mammal feature that many other animals lack.
Mammal species are split into three main groups: monotremes, placentals, and marsupials.
In general, mammals have been the dominant land animals for over 160 million years.
Monotremes lay eggs and suckle their young. Marsupials include animals such as kangaroos, koalas, and opossums that all live in Australia. Placentals are a very diverse group including animals such as whales, bats, horses, rabbits, humans and many others.
Mammals have a highly evolved four chambered heart which pumps blood to the body and lungs.